添加配置
配置pom.xml
在pom.xml中添加druid连接池、MyBatis框架、MySQL驱动的依赖:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.21</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
|
解决生成后mapper.xml丢失问题
在xml的<build>标签中添加以下内容,否则生成后的文件mapper.xml会丢失:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| <resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
</resource>
</resources>
|
配置application.properties
在application.properties中配置连接池和Mybatis主配置文件的位置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello_mysql?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.datasource.initialSize=10
spring.datasource.minIdle=10
spring.datasource.maxActive=50
spring.datasource.maxWait=60000
mybatis.config-location=classpath:mybatis-config.xml
|
这里的部分连接池配置不会生效,因为spring boot的默认配置中并没有这些配置项,为使其生效,我们需要创建一个新的类,这些我们之后再说。
配置mybatis-config.xml
MyBatis的配置规则还是不变,具体了解可以翻阅笔者以前的文章,值得一提的是,这里我们 使用package来指定存放mapper的包
,进行统一扫描:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url"
value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello_mysql?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<package name="org.koorye.hellospringboot.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
|
配置generatorConfig.xml
规则还是和以前完全相同, 注意此处xml文件的命名必须如此且直接放在resource目录下 ,这是spring
boot的默认配置(如果要修改文件名和位置请自行修改配置):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd"> <generatorConfiguration>
<classPathEntry location="D:\software\system\mysql-8.0.19-winx64\lib\mysql-connector-java-8.0.19.jar"/>
<context id="MysqlGenerator" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello_mysql?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC"
userId="root"
password="123">
</jdbcConnection>
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="org.koorye.hellospringboot.pojo" targetProject="src/main/java">
<property name="constructorBased" value="true"/>
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="false"/>
<property name="immutable" value="false"/>
<property name="trimStrings" value="true"/>
</javaModelGenerator>
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="org.koorye.hellospringboot.mapper" targetProject="src/main/java"/>
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="org.koorye.hellospringboot.mapper"
targetProject="src/main/java"/>
<table tableName="user"/>
</context>
</generatorConfiguration>
|
添加连接池配置类
我们之前说过,application.properties里的部分配置是不生效的,例如:
1
2
3
4
| spring.datasource.initialSize=10
spring.datasource.minIdle=10
spring.datasource.maxActive=50
spring.datasource.maxWait=60000
|
要使其生效,我们需要实现一个配置类。
在config包内新建一个DruidConfig类,使用@ConfigurationProperties读取配置文件,prefix用于指定前缀,之后再用@Bean将其加入组件。
然后我们再配置Druid后台监听器,新建一个map用于存放用户名和密码,将其存入ServletRegistrationBean组件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package org.koorye.hellospringboot.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druid() {
return new DruidDataSource();
}
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet() {
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
Map<String, String> initParams = new HashMap<>();
initParams.put("loginUsername", "admin");
initParams.put("loginPassword", "admin");
bean.setInitParameters(initParams);
return bean;
}
}
|
然后,我们就可以通过localhost:8080/druid/login.html访问后台啦:


MBG逆向工程生成代码
在右侧Maven的Plugins中找到mybatis-generator,双击运行mybatis-generator:generate:

解决逆向生成xxxKey和xxxwithBlobs的问题
网上的说法是如果你的数据表中有text类型的列就会生成这xxxKey和xxxwithBlobs,笔者的数据表中并没有text类型却还是生成了。
虽然不知道原因,不过我找到了解决方法。在generatorConfig.xml的<jdbcConnection>中加入一项property:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| <jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hello_mysql?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&serverTimezone=UTC"
userId="root"
password="123">
<property name="nullCatalogMeansCurrent" value="true"/>
</jdbcConnection>
|
这样生成的代码就只有xxx和xxxExample啦:

使用MBG生成的代码访问数据库
笔者此处采取接口和mapper同包的结构,因此要分别配置接口和mapper的位置。
扫描mapper接口
在spring boot主程序上添加注解@MapperScan并指定mapper接口的位置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| package org.koorye.hellospringboot;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@MapperScan("org.koorye.hellospringboot.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloSpringbootMybatisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloSpringbootMybatisApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
扫描mapper.xml
在application.properties中配置mapper.xml的位置
1
| mybatis.mapperLocations=classpath*:xxx/xxx/xxx/mapper/*.xml
|
实现访问数据库的控制器
常规方法,通过流读取主配置文件,再通过SqlSessionFactory得到session和mapper,此处使用static来避免每次访问数据库都生成一次。之后依然是MBG的常规用法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| package org.koorye.hellospringboot.controller;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.koorye.hellospringboot.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.koorye.hellospringboot.pojo.User;
import org.koorye.hellospringboot.pojo.UserExample;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Controller
public class UserDataController {
private static UserMapper mapper;
private static SqlSession session;
static {
try {
InputStream stream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(stream);
session = factory.openSession();
mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
} catch (Exception event) {
event.printStackTrace();
}
}
@RequestMapping("/user/list")
public String view(Map<String, Object> map) {
UserExample example = new UserExample();
example.createCriteria().andIdIsNotNull();
List<User> userList = mapper.selectByExample(example);
map.put("userList", userList);
return "list";
}
}
|
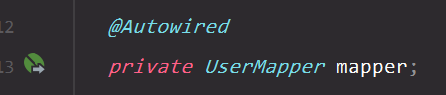
自动装配mapper
上面的方法是按照MyBatis的方法手动读取配置文件获得mapper,不过spring
boot可以直接通过@AutoWired得到mapper,然后就可以访问数据库啦:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| package org.koorye.hellospringboot;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.koorye.hellospringboot.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.koorye.hellospringboot.pojo.User;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserMapper mapper;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
User user = mapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1);
System.out.println(user.getId() + user.getName());
}
}
|
结果正常输出:

关于@Autowired报红
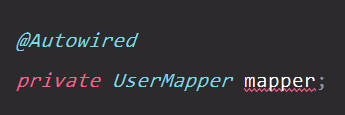
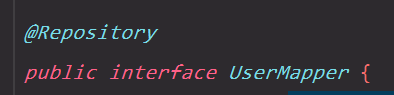
只需要在mapper的接口上添加@Repository注解,就不会报红啦: